Plant-based Eating
Currently, there is no exact definition of plant-based eating, yet many people associate it with a vegetarian or vegan eating pattern, which is not necessarily the case. Whilst plant-based diets shift the balance in favour of plant foods, they do not have to eliminate all animal products. Plant-based eating encompasses an array of eating patterns which are predominantly based on healthful plant foods whilst consumption of animal foods is reduced or excluded. Examples of plant-based eating patterns include the Mediterranean diet as well as the Eatwell guide, where plant foods, including plant proteins, are prioritised. Plant-based eating, whether it includes smaller quantities of animal foods or solely based on plant foods, has been proven to significantly improve health and be better for the environment.
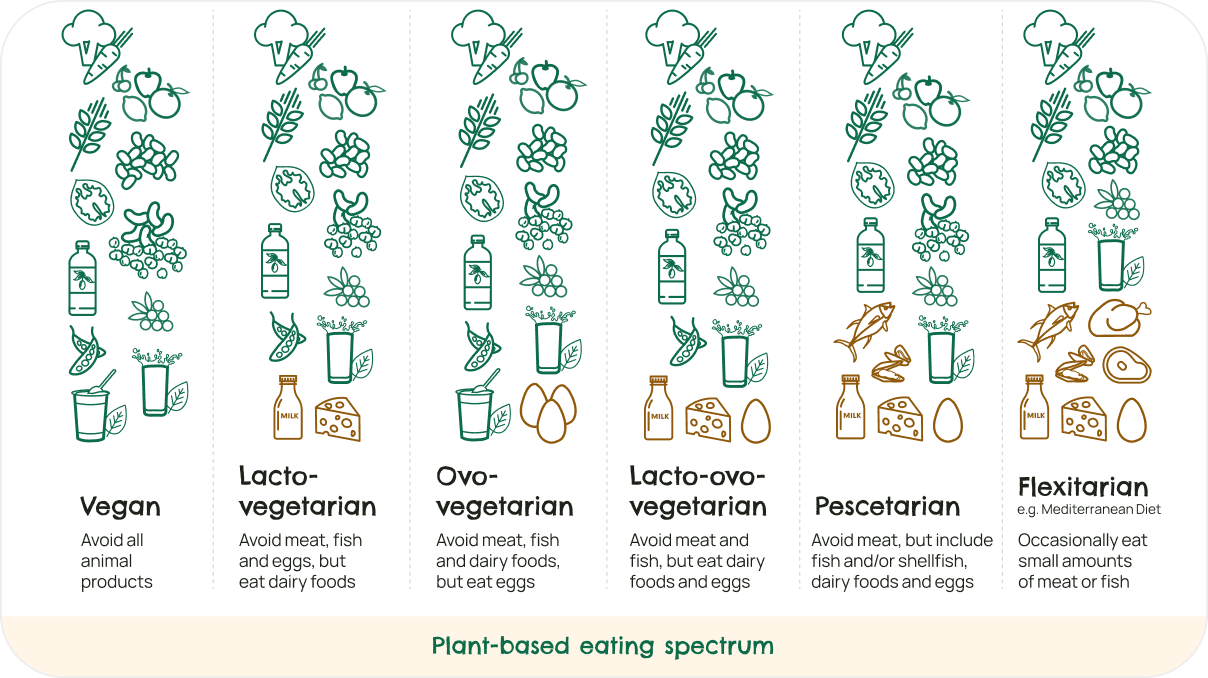
The health benefits of plant-based diets have been attributed not only to the lower intakes of red and processed meat and high saturated fat animal products, but also to the increased quantity of healthful plant foods. Plant foods provide fibre, vitamins and minerals and tend to be less energy dense and are lower in saturated fat compared to animal foods.
Additionally, it is now well established that diets which are based predominantly on plant foods have positive impacts on the environment and are more sustainable.
The proven health and environmental benefits of plant-based eating have shaped many national and international dietary recommendations.